德国虚拟博物馆的发展
虚拟现实历史建筑的互动4D重建
A ‘virtual museum’ (VM) has the potential to greatly improve the experience of a traditional museum visit, adding the possibility to provide information in a new, entertaining and convenient way. Interactive digital visualisations in particular can increase the comprehensibility of a complex topic. Such an application has now been developed as part of a master’s thesis for the Museum Alt-Segeberger Bürgerhaus in Bad Segeberg, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The whole building, the museum exhibition and six historic stages of construction have been reconstructed based on the capture of 3D data. Visitors can explore the historic building in a real-time 3D environment, both in a desktop application and in virtual reality (VR).
Alt-SejebergerBürgerhaus是Bad Sejeberg最古老的建筑。在1541年建造的建筑物在475年历史中,该建筑物已经改变了其形式和功能多次。与博物馆的历史学家和博物馆的历史学家和负责人合作,有可能在六个主要的建设期间确定建筑物的外观。这是一座小型的三室内的小房子,在1534年被摧毁了大部分城镇,包括以前的建筑物,在1534年。几个世纪以来,随后将几个房间添加到建筑物中。门面和室内设计符合相应时代的需求和可能性。最后一次重大改造于1963 - 64年,第一次在建筑物中建立了一个博物馆。自2012年以来,它一直在展示展览城市和建筑物的历史以及德国文化(图1)。
Since 2011, there has been a cooperation between the museum and the HafenCity University Hamburg (HCU), whereby the museum building has been used in the practical education of students from the HCU’s bachelor programme in geomatics. Students have recorded both the exterior and interior of the building and created 3D models for the purpose of learning photogrammetric 3D recording and visualisation techniques. This data forms the basis for the VM project.
3D modelling
第一步是基于上述数据构建其当前状态的建筑物。为了优化性能,模型未通过点云计算,而是在AutoCAD中手动构造。因此,即使在标准计算机上,也可以实现用于可视化的稳定的帧速率,同时仍然具有在场景中包括的体积相当于包括在场景中的重要对象细节。
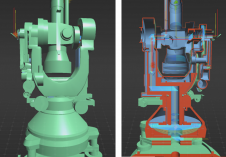
使用当前状态的模型作为起始点并通过历史源重新检测每个已知的重建变化的步骤和回溯每个已知的重建变化(图2)的步骤来创建历史模型。此外,博物馆周围环境中的建筑物被建模,以非纹理,简单的几何形状,为站在博物馆外的游客提供环境背景。此外,展览的最重要部分是为后来的融入建筑内部而建模的。所有对象的总三角形数量为大约100,000个三角形,这对于低成本,实时可视化应用是一个很好的基础。
游戏引擎和编程
互动部件是使用虚幻引擎4游戏引擎开发的。游戏发动机为实时渲染和不断增加的虚拟现实系统的支持提供了非常高的性能。对于桌面版本,建筑物内外,几个固定位置被放置在建筑物内外。用户可以从任何位置自由浏览,并且可以在带有短动画过渡的位置之间切换,或者可以通过单击微型概览地图上的所需位置来使用直接传送。与环境的交互是由共52个可点击的信息标志提供的。每个符号打开一个菜单,其中包含有关感兴趣对象的更多信息。菜单通常包括文本和相当大的照片(图3)。还可以在菜单中实现其他媒体,例如视频和单独的小3D模型。
VM的主要特征是施工历史的可视化。设计为型号内的“模型”,可以通过围绕它们行走并激活提供各种施工状态的爆炸视图的动画来探索建筑物的历史型国家(图4)。或者,可以从一个状态到下一个州的建筑物外观的个体变化伴随着关于施工期间主要变化的评论。
虚拟现实
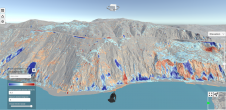
VM的VR版本使用HTC Vive创建,自2016年4月以来已在市场上提供。固定职位由自由导航替换,无论是通过传送还是直接行走。两个运动控制器也用于与环境进行互动;一个控制器满足传送功能,并包含激光束以激活和与菜单进行交互,而另一个控制器包含菜单屏幕和微型概览地图。透视自由和改善的规模感使VR博物馆成为一个沉浸式3D环境。这允许通过给游客在它们周围改变时实际上站在建筑物内部的可能性(图5),更深入地分析了建筑物的演变的4D模型。
结果与结论
该程序的最终桌面版本的大小为500MB,可在Windows-OS上可执行,无需软件安装。这将应用领域从博物馆本身扩展到大多数个人计算机(PC),使访问者能够购买该计划并进一步深化他们对他们所看到的展览主题的了解。
The VR version of the program has been demonstrated on several occasions, including at Intergeo 2016 in Hamburg. The very positive feedback showed the promising potential of such applications, which is particularly high in – but not limited to – the museum context. In theory, any application which benefits from a realistic representation of the environment and is improved by an immersive experience can benefit from the use of interactive VR. This can increase the entertainment aspect, a person’s understanding and their motivation to deal with an unknown topic, and the approach can help to convey information in presentations, promotional and/or educational settings.
Further Reading
- Kersten, Th., Tschirschwitz, F., Deggim, S., 2017. Development of a Virtual Museum including a 4D Presentation of Building History in Virtual Reality.摄影测量,遥感和空间信息科学的国际档案,XLII-2 / W3,3D虚拟重建和复杂架构的可视化,2017年3月1日至3日,NAFPLIO,Greece,编辑:D.Aguilera,A.Georgopoulos,T. Kersten,F. Remondino和E.Stathopoulou,
- 361-367。Kersten,T.,Hinrichsen,N.,Lindstaedt,M.,Weber,C.,Schreyer,K。,Tschirschwitz,F.,2014年。由摄影测量,陆地激光扫描和陆地激光扫描和陆地激光扫描和陆地激光扫描的建筑历史4D文档历史分析。在:文化遗产进展。计算机科学的文档,保存和保护,讲义笔记(LNCS),8740卷,斯普林克国际出版瑞士2014,35-47
- Tschirschwitz, F., Kersten, Th., Zobel, K., 2014. Interactive 3D Visualisation of Architectural Models and Point Clouds Using Low-Cost-Systems. In:文化遗产进展。计算机科学的文档,保存和保护,讲义笔记(LNCS), Volume 8740, Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2014, 268-278.
关于the Authors
Simon Deggim
Simon Deggim completed his master of science degree in geomatics at the HafenCity University Hamburg in 2016. Since October 2016 he has been a member of the academic staff of the same university, working in the field of visualisation and VR projects.
Felix Tschirschwitz.
Felix Tschirschwitz是汉堡哈菲特大学的一名研究助理。He obtained his bachelor’s and master’s degrees in geomatics from the same university and has been working with interactive visualisation since 2013.
托马斯P.克斯滕
托马斯P.Sersten自2001年以来,托马斯P. Kersten为Bachelor和硕士学位的汉堡汉堡汉堡博物馆学习计划是一名全面教授。他是同一个大学的摄影测量和激光扫描实验室的负责人。
让你的收件箱更有趣。Add some geo.
Keep abreast of news, developments and technological advancement in the geomatics industry.
免费注册