Seeing the Future: AI, BIM and Digital Twins
Digital Construction Week 2019
本文最初发表在地理学世界.
During Digital Construction Week (DCW), which was held at the Excel in London from 16-17 October 2019, there was one seminar stream on geospatial surveying and two specifically on building information modelling (BIM). But relevant topics such as artificial intelligence (AI) and visualization, as well as BIM, cropped up in many of the other sessions. The most used buzzword was 'digital twin',which was heard in many talks and in the exhibition booths.
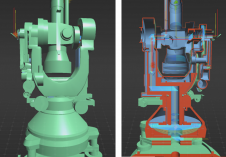
The term digital twin is used quite flexibly, but essentially it implies that an object must have a digital representation which can be presented visually, i.e. a virtual object. At a more advanced stage, the components of the object, represented digitally, can be controlled and updated and can be interrogated in real time. They can be linked to the Internet of Things (IoT) and analysed with artificial intelligence (AI), usually operating in the cloud.
So, what are the main developments and what is their impact on construction and, in particular, geospatial practice?
A presentation on the Main Stage by Anne Kemp (Atkins and the UK BIM Alliance) gave an excellent summary of the current position. BIM is clearly a driving force and new publications from the UK BIM Alliance set out theframework和stress the need for a common framework and for standards. The relevant publications are the second edition of Guidance Part 2: Processes for Project Delivery with additional insight on the activities associated with ISO 19650-2 clause 5; and the updated Guidance Part 2. The UK BIM Framework is also releasing revised guidance for the public sector on applying BS8536 parts 1 & 2 – Government Soft Landings.

国家数码双胞胎
It is essential that all partners in the construction/build/maintenance cycle speak the same language and avoid confusion and this becomes even more important when we consider the ambitions of a digital twin. The objective of a (UK) National Digital Twin involves connected digital twins creating an ecosystem, embracing transport, energy and the built environment.
The双子座原则support this through requiring a clear purpose, being trustworthy and functioning effectively. The concept of the Golden Tread, linking all changes in a building, was held up as an ideal which could have saved lives in the Grenfell Tower disaster.
All of this is promoted and developed by The Centre for Digital Built Britain (CDBB) which is a partnership between the Department of Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy and the University of Cambridge, to deliver a smart digital economy for infrastructure and construction for the future and to transform the UK construction industry’s approach to the way we plan, build, maintain and use social and economic infrastructure.CDBB被呈现为开发这种数字Nirvana的组织,这可能有助于降低碳足迹并降低空气污染。
Artificial Intelligence
AI是会议和研讨会中的另一个主要话题,并且被问到的重要修辞问题是'机器人可以做什么?'这几乎没有答案。成功Ai的具体例子是英国初创公司Vercator. David Selviah from Vercator discussed the problems of extracting information from scans and the challenge of processing big data. He did, however, show that AI could identify features from point clouds such as planes, edges and specific objects such as chairs. He also painted an optimistic picture of future research and stressed the value of the cloud to speed up processing and store large volumes of data.
Matt Armstrong-Barnes from HPE stressed that AI needs to be used appropriately and that it is particularly good at finding anomalies and for identifying safety issues on construction sites. It has been shown to be very effective at spotting defects in aluminium.
A survey has shown that 40% of digital companies see AI as essential. He said that much work has been done but that it needs to be put together to solve problems.

InSAR and BIM
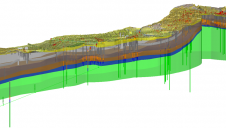
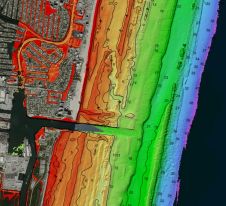
来自Telespazio的Maria de Farago在使用SAR干涉测量中提出了发展。De Farago演示了如何使用Excel附近的开发地点用于结构健康监测(SHM)和资产管理。insar数据可以集成到BIM模型中。这涉及不含原位仪器,可以测量构建变形到厘米水平。INSAR监控也可用于预测LAMESLIPS。
Many geospatial companies were present at the exhibition including Bentley, Bluesky, FARO, GetMapping, Hexagon, Korec, Leica Geosystems, Murphy Surveys, Plowman Craven and Skanska. Companies such as Royal Haskoning DHV offered services in the fields of aviation, buildings, energy, industry, infrastructure, maritime, mining, transport, urban and rural development and water, and set great store by the digital transformation and supporting a sustainable environment.
Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality were centre stage during the Visualization Track of the seminar programme, proving that both technologies are more than just a buzzword. VR can be a fantastic tool for training purposes; however, the isolated nature of VR headsets is not always a very suitable solution. Igloo Vision demonstrated a different way: shared VR in projection domes or cylinders, allowing for whole teams to be immersed not just in training scenarios but also in BIM.
虽然许多专业人士越来越熟悉VR and AR, mixed-reality is less mainstream. Augmented reality is delivered through a handheld mobile device (a smartphone or a tablet); mixed reality is delivered through head-mounted see-through glasses. Mixed Reality is a fusion of real and virtual worlds, enabling the production of new environments and visualizations where physical and digital objects co-exist and interact in real time.
Keltbray是一家领先的英国土木工程集团,证明了他们如何将微软Holdens混合现实凭证纳入其规划和建议的发展阶段。由于这种前瞻性思维方法,他们能够在早期阶段提升和优化过程,降低成本和效率低下,允许开发人员和服务提供商之间的协作环境。

结论
Overall, the exhibition and presentations atDigital Construction Week可以被视为在这里和现在之间的二分法,其特点是仪器公司和调查公司,旨在通过利用数字技术来赚钱支持建筑业的资金,并希望在未来赚钱。188asia备用网址由于建筑,工程和建筑(AEC)行业的许多承包商在接受数字转型时滞后,地理空间世界仍然存在许多机会。
让你的收件箱更有趣。Add some geo.
Keep abreast of news, developments and technological advancement in the geomatics industry.
Sign up for free