Mobile Lidar for Urban Streetscapes
Mapping Historic Sixth Street in Austin, Texas
测绘,Inc .(山姆,Inc .)执行a mobile Lidar survey of the historic Sixth Street district in Austin, Texas, USA, for an urban planning project being conducting by the municipality. Sixth Street is an acclaimed music and entertainment district in the heart of downtown Austin, and city planners intend to redevelop it, broadening the pedestrian streetscape and improving both vehicular and pedestrian traffic control. Using mobile Lidar technology to survey this busy street significantly shortened data acquisition time and provided survey-grade deliverables to the city. The detailed point cloud dataset was also made available to city planners for 3D planning and visualisation.
In 1996, the City of Austin, Texas, began work on its Great Streets Master Plan project to improve the quality of downtown streets by transforming the public right-of-way into public spaces that were accessible and comfortable, with an aesthetic pavement network throughout. As the City of Austin Planning and Development Review Department stated in its vision, “A community’s downtown is the heart of that community, and its streets are its primary public spaces for downtown life and commerce.” A typical Great Streets layout included pavements 18 or 32 feet (5.5 or 10 metres) wide, street furnishings such as benches, bike racks and litter bins, and contiguous canopy of mature trees to provide shade. After discussions between the city’s planning staff and a local non-profit organisation comprising property and business owners in the historic Sixth Street corridor, the city began preliminary planning for the East Sixth Street corridor in keeping with the Great Streets plan.
This historic streetscape includes rich and varied architecture, so any work to expand pedestrian facilities would require careful integration with the existing buildings. It was crucial to the City of Austin planning staff that they had detailed and accurate information of all visible, above-ground street features (including drainage, water, wastewater and storm sewers), and they had a particular need to be able to identify the various paving materials, details of buildings’ facades, column-supported overhangs and floor elevations for all building entrances.
SAM, Inc. was contacted by the City of Austin to perform a design survey of seven blocks of East Sixth Street in downtown Austin, including five intersecting streets. During initial project planning discussions, City staff expressed concerns about accessibility and safety when working on this project in active downtown streets.
使用传统服务收集这些信息ying techniques would require time-consuming and costly closures to traffic lanes for an extended period of time. In view of the high level of detail the City needed for this dense urban environment and the potential accessibility and safety issues involved in working at the project site, it was clear that using mobile Lidar mapping technology could address these concerns and deliver value to the City.
Mobile Lidar
Mobile Lidar is an innovative mapping solution that incorporates the most advanced Lidar sensors, cameras and position/navigation equipment to collect survey-quality point data quickly and accurately. SAM’s mobile Lidar vehicle utilises two 360-degree Lidar sensors, two five-megapixel cameras, two GPS receivers and an Inertial Measuring Unit (IMU) to provide data density of up to 1,600 points per square metre, depending on system settings. This non-invasive method of surveying can be operated day or night and collects millions of 3D points per minute, allowing for faster coordinate acquisition that far exceeds the efficiency of traditional survey methods.
Mobile Lidar technology is ideal for projects requiring an extraordinary level of detail, such as streetscape design. The accurate point cloud datasets offer a ‘complete picture’ of the project site and can be processed for survey-grade deliverables, 3D visualisation and modelling and other project needs without additional mobilisation costs. Using mobile Lidar technology, the survey-grade data the City needed was collected in a fraction of the time it would have taken conventional surveying methods. Since data was collected remotely and in early morning hours, removing the need for traffic diversion required by traditional surveying activities, the system also provided increased safety for project personnel and the general public. The value this unique technology provided to the City and the forward-looking potential uses of the data proved an excellent fit.
Project Control
In order to achieve the survey-grade accuracy required for this topographic design survey, SAM recovered and used primary survey control data provided by the City of Austin Engineering Services Division (NAD83/93/NAVD88 values [Texas State Plane, Central Zone]) and SAM field crews set secondary control targets at each block. The secondary controls acted as observed targets during the mobile data collection so that their known locations could be used to calibrate the point data.
Data Collection
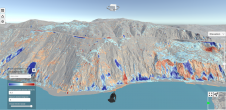
This seven-block area of East Sixth Street is at the heart of Austin’s downtown entertainment district. Restaurants and music venues draw heavy foot traffic on the pavements while the street provides vehicular access to many downtown businesses. This density of pedestrian and vehicular traffic presented a challenge of access for both field personnel and Lidar data capture. To address this challenge, mobile Lidar data collection was scheduled for early on a Sunday morning to minimise potential obstructions (pedestrians or vehicles that could create data voids in the Lidar point cloud). SAM, Inc.’s mobile Lidar vehicle arrived at the project site at dawn and the data acquisition was complete less than four hours later, during which time technicians had collected more than 3.7 billion data points along the project corridors and over 20,000 georeferenced digital images (collected at three frames per second).
数据游行
For the benefits of mobile Lidar to be fully realised, the surveyor must effectively manage the huge amount of data collected and extract precisely what the client needs in the required format. As one of the first firms in the U.S. to add mobile Lidar to its collection of services, SAM was able to deploy tested workflows to efficiently process Lidar into a final product specific to the City’s needs.
Using disk extraction software, SAM mobile mapping technicians downloaded the laser range data and digital images. Raw trajectory data were also downloaded from the system operation laptop. The company then produced a smoothed best estimate of trajectory (SBET) using positional data collected by the mobile Lidar system (GPS, IMU and DMI), which correlated with the primary and secondary controls collected at the project site. Using software that geospatially references the laser data to the trajectory through a time relationship, LAS files (a public file format for the interchange of 3D point cloud data) were created and calibrated to ground-control targets. Mobile mapping technicians then used specialised software to organise and manage the files and to tie the laser scan data to the ground-control data for improved geometric accuracy.
Final Deliverables
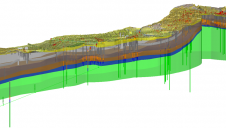
通过创建受控和更正的数据集,移动映射技术人员开始提取过程,以收集项目区域内的所有相关功能:地上和可见的街道,排水,水线(阀,仪表,仪表,仪表,人孔,水卸物和水液)), wastewater and storm sewer features, detailed data from the buildings’ facades, the location of column-supported overhangs and building entrances facing the street, including all steps and finished floor elevations. Miscellaneous features such as signs, utility poles, guy anchors, overhead power lines, traffic control facilities and utility appurtenances were also located.
The extracted topographic survey information was processed and delivered in Autodesk Civil 3D, using the City of Austin’s ESD CADD Standards, drawn on the appropriate level and in the format required by the City. This allowed the data to be seamlessly integrated into the preliminary engineering design efforts for the City.
Added Value
虽然不是最初工作范围的一部分,但在东六街收集的LiDAR数据集将自己借给许多其他可能为城市提供附加值的应用程序。在这个七个街区区域中收集了超过37亿个数据点,该密集详细的数据集可以挖掘出未来的需求,而无需其他动员或数据收集。移动激光雷达也可用于3D可视化项目计划。在这种情况下,设计过程中的利益相关者在内,包括工程师,建筑师和市政工作人员以及可能是公众 - 可以在3D中查看和浏览项目区域,这提供了对项目详细信息和进度的增强理解。此外,通过补充处理和操纵,该数据集可以呈现为项目位置的详细,颜色的3D模型,显示建筑物外墙的独特架构细节。该模型可以与整个设计阶段的建筑计划集成在一起,以使设计师和城市对增强的街景进行现实描述。
概括
Using mobile Lidar technology, SAM was able to deliver a highly accurate topographic survey of a dense urban environment. The data was collected in a fraction of the time it would have taken using conventional survey techniques, without costly lane closures and with no danger to field crews or the public. Additionally, the detailed dataset can be used for 3D visualisation and modelling and other project needs without additional mobilisation costs.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to the members of the City of Austin Public Works Department for their forward-thinking approach to
this project.
Make your inbox more interesting.Add some geo.
Receive a weekly summary of the biggest news, along with the best stories, case studies, and key market insights.
Sign up for free