GNSS,日as和无人机
This article was originally published inGeomatics World。
Richard Groom summarises some of the interesting papers from the FIG Congress focussing on GNSS, Hydrography, 3D Cadastre and mapping.
GNSS – Detecting Cycle Slips
罗伯茨(Roberts)和汉考克(TS03E)(TS03E)在多构造和多频世界中介绍了有关GNSS可观察物的论文。本文以有关系统如何开发的有用摘要开始。具体而言,他们查看范围残留范围和电离层残差 - 两者都可用于检测循环滑动。
The range residual is the difference between the range calculated using pseudorange and the range calculated from the carrier phase on a specific frequency for consecutive epochs. It is a direct measurement of noise, because all other factors, such as ionospheric and tropospheric errors are treated as the same over the very short time interval.
For signals passing through a vacuum, the phase observations from a satellite to a receiver can be mathematically scaled to determine the equivalent phase measurement on another frequency. GNSS signals actually pass through the ionosphere and the effects of the ionosphere appear as residuals between phase which would be expected in a vacuum and the phase actually observed – known as the ionospheric residual.
作者绘制了所有星座中各种卫星的电离层和范围残差,结果使观看变得有趣。他们指出,来自GPS,Beidou和Galileo的L1,B1和E1信号总是比其他频率更嘈杂,并且在低海拔时噪声更大,来自较新卫星的信号比较旧的卫星表现出较少的噪音,即使在同一星座中也显示出噪音。,一些卫星比其他卫星产生的质量数据更好。
在同一主题,赵et al (TS03E)描述how the triple frequency GNSS, now available, can be used to detect and correct cycle slips instantaneously by comparing the process of cycle slip detection for single, dual and triple frequency receivers. This extends the latency of fixed ambiguities, shortens the convergence time for precise point positioning and improves the positioning precision of the carrier phase. For the user, the results should mean greater reliability and higher accuracy. This method works well for satellites above 20° elevation. There is still further work to be done to detect cycle slips below this elevation.
Gao (TS04E) states that it is just a matter of time before precise GNSS enters the mass market. Mass market receivers which process carrier phase measurements are being introduced but the challenge is to reduce convergence times from tens of minutes to be almost instantaneous.
Luo et al (TS04E) goes into some detail on the means of adjusting GNSS observations when the pole is tilted. Determining the direction to north is the challenge. If an electronic compass is used it will be disturbed by local magnetic effects, so Leica’s GS18T utilises IMU measurements. By tilting the receiver, the range to satellites changes as does their elevation angle.
Hydrography
在TS01D会议上,Abadallah和Schwieger测试GNSS PPP(精确点位置)用于河流的水文调查。通过保持高度坐标固定,可以提高2D位置精度。他们的RMS为47-80mm。约束位置比无约束位置少16-35%。
As the political temperature in the South China Sea continues to rise, Abdullah (TS01D) discusses how to determine the position of the edge of the continental shelf. Under UNCLOS, this is defined as the change of gradient between the continental slope (typically 2 to 45°) and the ‘rise’ (typically less than 0.5°). He traces a line around an area known as “The Dangerous Ground”, the disputed part of the South China Sea, which is characterised by many isolated reefs, rocks and islands.
Ugwuoti et al presented a study of the effect of beam width and sea bed slope on the accuracy of bathymetry to IHO Special Order and Order 1a and 1b. They present their results in tabular form.
Best Practices 3D Cadastres
TS04C致力于六个演讲 - 介绍,然后是无花果出版物的五章“最佳实践3D神学院”。Van Oosterom的论文介绍了有关法律基础的五章,包裹的初始注册,3D会计信息建模,3D空间DBM和可视化。完整的文档可以从中下载www.fig.net/resources/publications/figpub/FIG_3DCad/FIG_3DCad-final.pdf
第一章首先的一点development of 3D spaces above ground, with high rise and overlapping rights restrictions and responsibilities, and underground with basements, tunnels and utilities, 2D cadastral records are no longer suitable. However, the concept of 3D varies according to the legal history of the country concerned. The chapter examines the situation in 15 countries around the world and with varied civil law backgrounds and ranging from countries which already have 3D cadastres to those where 3D has not been considered. Chapter 1 is itself a mighty work of 70 pages but pages 54 onwards compare the examples and summarises the findings.
第2章考虑正在注册的内容。例如,它可能是一个物理结构,一个包围物理3D结构的信封或地面上方或下方的一部分权利。目的是具有权威,使用开放格式并符合国际数据建模标准。比较八个国家的3D财产定义。本文考虑使用BIM等来源生成模型。
Chapter 3 covers cadastral information modelling and the linking of rights, restrictions and responsibilities modelled using the Land Administration Domain Model (LADM) with physical reality. The authors acknowledge that land ownership boundaries and physical features are linked, and the value of taking data from existing physical models, but note that these have to be ‘as built’ as opposed to design data. They also point out the risks should the physical object move. The authors look at compatibility between Smart City, BIM and indoor data (expressed in IndoorGML) and legal boundaries. They compare the approach in five countries and wind up with some useful conclusions.
第4章介绍了3D神经区的3D空间DBM,并以“如何处理点云以及3D对象”的问题开头。作者意识到点云用于可视化和测量物理特征的值。作者还考虑使用“体素”,该“体素”使用网格立方体定义3D空间。数据存储是一个问题,本文描述了“镶木”格式。索引是空间数据管理的重要组成部分,文章为这个有趣的主题提供了足够的空间,然后是3D几何和操作。然后,本文研究了专有DBM如何处理3D会长数据。如果对于我们大多数人来说,59页的文章太长了,那么第49页的结论非常值得阅读。
可视化的最后一章包括另外55页的智慧,值得一读。3D神学院有很多用户,论文考虑了这些用户组,他们的需求和挑战。与其他论文一样,作者强调需要牢记4D和3D的必要性。
UAVs, Laser Scans and Radar
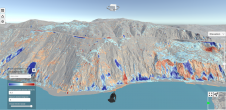
Weber and Lerch (TS02F) provide a very useful comparison of height accuracy for surveying a quarry using the Trimble SX10, which was used as ‘control’ and various configurations of UAV photogrammetry using the SenseFly eBee. Photogrammetric computations were made with the eBee’s RTK positioning facility - with and without using ground control points. This is a ‘must read’ for most of us.
Combining terrestrial laser scanning with UAV photogrammetry for low cost surveying is the subject of Afifi and Rabbany (TS04F). The scanner was a FARO Focus S and the UAV was a DJI Phantom 4 Pro with a 20Mpx camera with 84° field of view. They flew a grid of flight lines with two circles around the perimeter of the site. There were eight ground control points and 16 verification points which revealed altitude errors between -4.8cm and +4.2cm.
无人机photogrammet Altinisik和Kavlak (TS04F)使用ry to survey progress in construction of a railway line in Ehtiopia. The intention was to check for setting out errors and calculate progress volumes for payment. Ground control was established at 500m intervals along the 270km long 80-340m wide corridor. A fixed-wing UAV was used carrying a Sony A6000 camera. Output from the camera was in RAW format which could then be radiometrically corrected using CaptureOne software. The photogrammetry was carried out using Pix4D. The authors go into some useful detail about construction of the DSM.
Guney et al (TS04F) established a ‘semantic mapping framework’ to enable mobile robots to act intelligently in the environment and solve tasks. They used a robot equipped with a laser scanner to explore the environment and generate mapping with semantic information. The goal is to enable robots to perform a number of tasks, including inferring nearby objects, complex navigation and path planning, and change detection. It involves recognising patterns and learning new patterns in 3D. The authors go into some detail about how the data can be represented and labelled.
Cabuk et al (TS01C) studied open source DTM data from ALOS and SRTM satellites. They compared DTMs of hilly and plain areas. They concluded that ALOS 30m resolution data gives the higher accuracy (better than 2.5m). Continuing the open data theme, Shoman et al (TS01C), related their efforts to establish an open data initiative in Turkey.
这些论文可以从中下载www.fig.net/resources/proceedings/fig_proceedings/fig2018/techprog.htm
本文发表在2018年9月/10月的地球世界上