地震预测:新发现
困难的科学挑战
使用GPS分析预测地震仍然是一个未解决的问题但重要的问题。通过GPS接收器三角网络测量的面积预发信号,在日本和其他亚洲地区进行了许多大地震。我们发现,尽管可以预测地震的发生和位置,但在可以精确预测地震时需要更多的研究。
查看更大的地图
地震预测是科学最困难的问题之一。日本(图1)是一个易患灾害的国家;162年1月在2000年1月和2007年12月期间发生了162幅幅度ML> 6。因此,已经进行了很多关于地震预测的研究,但没有完全成功。自2003年10月在使用GPS的标题的地震预测下,我们在这里更新您的研究进度以来188金宝搏特邀一种基于GPS网络三角形的新方法。
背景
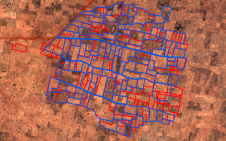
GPS网络三角形的方法由作者开发了2000年的作者。地理调查研究所(GSI)建造了5米高的塔,具有GPS天线,用于监测地壳运动。遍布日本各地的1,200个GSI GPS站(所谓的电子控制点)。这些天线收集的数据通过互联网上市可供公众使用。图2描绘了GSI GPS站,图3显示了GSI GPS站的分布。
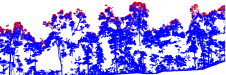
用于三角形网络预测的GPS站的选择基于相当粗略的间隔(20-50km),因为三角形跨越一个以上的构造板是重要的。无论距离如何,都以所选择的GPS站的所有可能组合形成三角形。从验证研究中,日本6,590个三角形被选中。每天检查由这些三角形跨越的区域进行超过一定阈值的变化。上述162个大地震在每次地震前一到九十天的时间内展示了预发信号,这取决于其类型。这证明我们可以预测地震的发生和位置,但不是它的时间。
虽然海外唯一的GPS站网络是国际GPS服务(IGS)提供的,但我们的方法还显示了位于震中附近的非常粗糙的网络的大地震的预发信号。下面讨论这些大地震的证据。
验证
在构建GSI GPS站后发生的每种地震都已经研究了预先存在的存在。彻底检查了表1(下文)中列出的大地震,这对基础设施造成严重损坏。不仅通过震中附近的小三角形检测到预信号,而且还通过非常大的三角形跨越不同的板,几千千克。
The Tokachi offshore earthquake was the largest during the study period, with a magnitude of 8.0 on the Richter scale (ML 8.0); although oil tanks were destroyed, there were luckily no casualties. Figure 4 depicts a typical pre-signal detected by a triangle one week before the occurrence, located near the epicentre. Pre-signals were detected 29, 23, fifteen, thirteen, twelve and one day(s) before the Miyagi offshore earthquake (of type 'inner plate'). The strongest pre-signals were found 23 days before the earthquake in 1,944 triangles, while pre-signals were found one day before the earthquake in 178 triangles. The epicentre is marked by a cross; red and blue lines show triangles including and excluding the epicentre. The Noto Peninsula earthquake demonstrated different behaviour to the Miyagi offshore earthquake. Except for one day before, pre-signals were detected in triangles both including and excluding the epicentre.
苏门答腊海啸
2004年12月26日发生的亚洲海啸有30万名受害者,由苏-Atra离岸地震(ML 9.0)引发。我们选择了震中周围的十个IGS GPS站,如表2所示(下面)。
We checked all possible combinations of triangles formed by these IGS GPS stations, investigating whether daily change in triangle area exceeded some threshold (0.05ppm). There was a drastic daily change of -1.2ppm in the YZ plane of the triangle of ntus-kunm-lhas (Table 2) from 18th December 2004, eight days before the earthquake. There was also a large change of -0.04, 0.05 and -0.05ppm in the XZ plane in the triangle of bako-ntus-lhas on the 21st, 22nd and 23rd December 2004, three to five days before the earth-quake. Although the distance between ntus (Singapore) near the epicentre and lhas (Lhasa) or kunm (Kunmin) is large, pre-signals were detected, highlighting the complexity of the crustal movement. These results imply that it should be possible to detect an early warning of such a huge earthquake.
四川地震
2008年5月12日,四川地震发生在中国四川省(中国吉姆国际吉姆国际中国四川地震1至3')。188金宝搏特邀以及许多约6万名受害者,地震摧毁了大量建筑和道路。震中周围只有四个IGS GPS站:武汉(WN),Xian(XN),kunmin(kn)和拉萨(LS)。连通拉萨,西安和武汉三角形的XZ飞机显示了2008年5月6日的三西格,地震前六天。这三角形包括四川地震的震中。虽然这个三角形如此大(最长的一面超过2,000公里),但地震的预警仍然有价值。
结束言论
使用来自GSI GPS站(日本)的数据以及有限数量的IGS GPS站(日本境内)检查了许多幅度ML> 6地震。GPS数据检测到每种地震前的预发信号。我们已经证明,可以预测震中的发生和位置;然而,预测发生的确切时间需要更多的研究。目前数据预测,在预发信号检测的一到九十天内发生地震。
Acknowledgement
由于东京电力服务公司为验证研究提供资金。
Table 1. Sample of large earthquakes investigated for pre-signals.
地震 |
震级 |
Date |
盘子 |
宫城近海 |
7.1. |
2003年5月26日 |
北美洲 |
托克希海上 |
8.0 |
2003年9月26日 |
北美洲 |
Niigata-Chuetsu. |
6.8 |
2004年10月23日 |
北美洲 |
西福冈海上 |
7.0 |
20 March 2005 |
欧亚 |
Noto Meninsula离岸 |
6.9 |
2007年3月25日 |
欧亚 |
表2.苏门答腊近海地震的震中周围的IGS GPS站。
IGP GPS. |
地点 |
经度 |
纬度 |
bako |
Cibinong,印度尼西亚 |
106.8500 E. |
6.4910 S. |
BAN2. |
班加罗尔,印度 |
77.5116 E. |
13.0343 N. |
coco |
科科斯岛,澳大利亚 |
96.8339 E. |
12.1883 S. |
dgar |
迭戈加西亚岛,英国领土 |
72.3702 E. |
7.2696 S. |
海德 |
海德拉巴,印度 |
78.5509 E. |
17.4172 N. |
Iisc |
班加罗尔,印度 |
77.5704 E. |
13.0211 N. |
昆明 |
昆明,中国 |
102.7972 E. |
25.0295 N. |
拉斯 |
拉萨,中国 |
91.1040 E. |
29.6573 N |
马尔德 |
马尔代夫 |
73.5263 E. |
4.1886 N. |
NTU |
新加坡 |
103.6799 E. |
1.3458 N. |